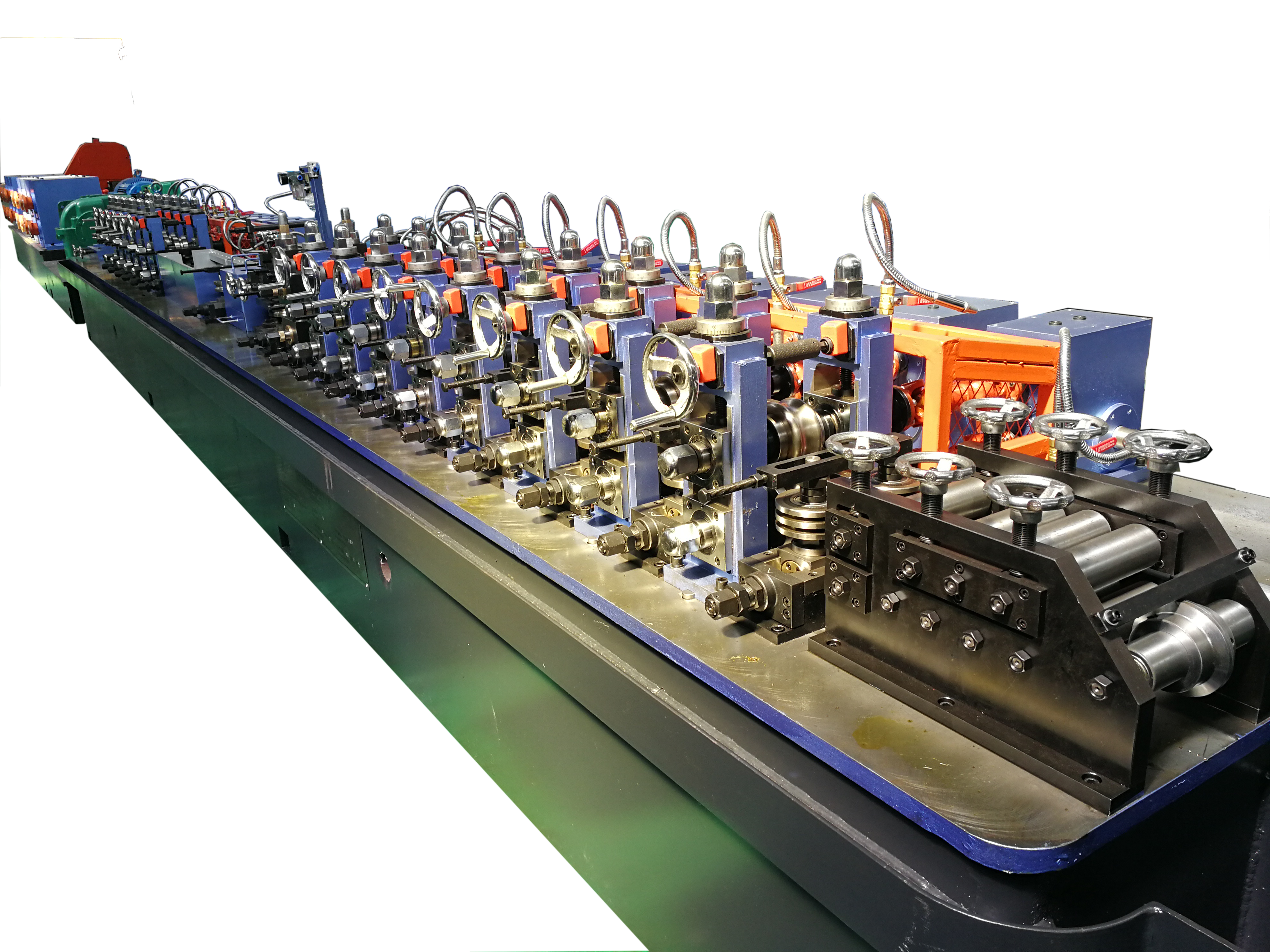
Understanding the Power of Modern ERW Tube Manufacturing
In the dynamic world of metal fabrication, ERW tube mills stand as a testament to engineering excellence and manufacturing innovation. These sophisticated machines have revolutionized the production of welded tubes, offering unparalleled efficiency and precision in creating essential components for various industries. From construction to automotive applications, ERW tube mills have become the backbone of quality tubular product manufacturing.
The electric resistance welding (ERW) process represents a perfect fusion of technology and metallurgy, delivering consistent weld quality and exceptional production rates. As industries continue to demand higher standards of quality and productivity, understanding the capabilities and operations of ERW tube mills becomes increasingly crucial for manufacturers and industry professionals alike.
Core Components and Operating Principles
Essential Mechanical Elements
At the heart of every ERW tube mill lies a series of precisely engineered components working in harmony. The entry section features an uncoiler and strip accumulator, ensuring continuous material feed. The forming section consists of multiple roll stands that gradually shape flat strip into a tubular form. Each roll stand is meticulously designed to apply the correct pressure and maintain proper alignment throughout the forming process.
The welding section incorporates sophisticated high-frequency welding equipment, complete with contact rolls and impedance coils. Following the welding station, sizing rolls and straightening units ensure the final product meets exact dimensional specifications. These components work together seamlessly to produce high-quality welded tubes with remarkable consistency.
Advanced Control Systems
Modern ERW tube mills feature state-of-the-art control systems that monitor and adjust every aspect of the production process. Digital controllers manage critical parameters such as line speed, welding temperature, and forming pressure. Real-time monitoring systems track product quality and automatically adjust operating parameters to maintain optimal production conditions.
Integration of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) allows operators to make precise adjustments and respond quickly to any variations in the manufacturing process. These advanced control systems significantly reduce setup time and minimize material waste while ensuring consistent product quality.
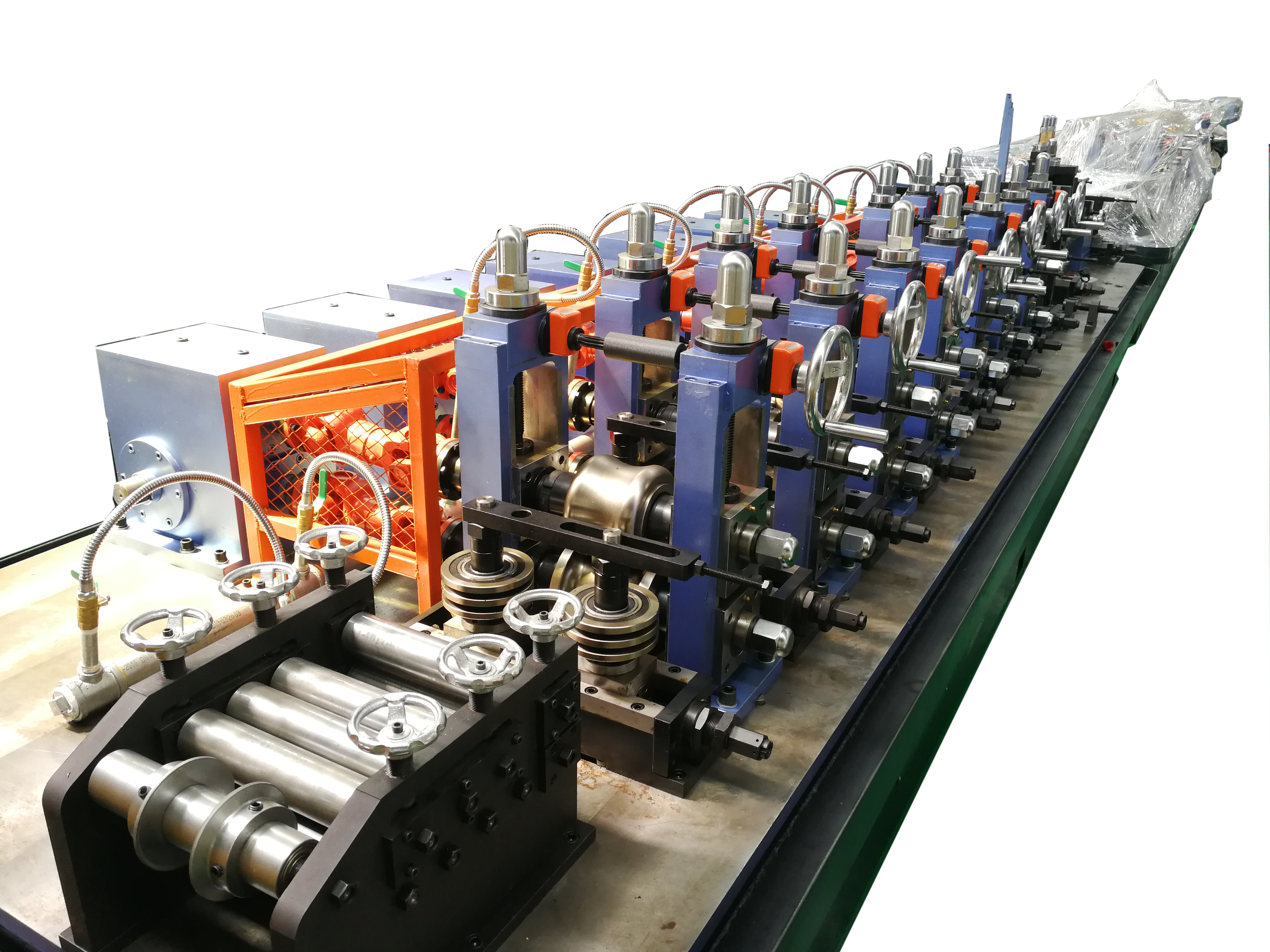
Production Capabilities and Applications
Size Range and Material Compatibility
ERW tube mills demonstrate remarkable versatility in terms of production capabilities. Modern mills can process tubes ranging from small diameters of 12mm up to larger sizes exceeding 660mm, depending on the specific mill configuration. Wall thickness capabilities typically range from 0.4mm to 12mm, accommodating various industry requirements.
These mills excel in processing different materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and various alloys. The ability to handle multiple material types makes ERW tube mills indispensable in producing components for diverse applications, from structural supports to precision mechanical parts.
Industry-Specific Applications
The construction industry relies heavily on ERW tubes for structural applications, including building frames, handrails, and support systems. The automotive sector utilizes these tubes for exhaust systems, chassis components, and structural reinforcements. In the furniture industry, ERW tubes provide both structural integrity and aesthetic appeal in various designs.
Agricultural equipment manufacturers depend on ERW tubes for irrigation systems and machinery components. The energy sector utilizes these tubes in oil and gas transportation, while the aerospace industry benefits from their precision and reliability in various applications.
Maintenance and Optimization Strategies
Preventive Maintenance Protocols
Implementing comprehensive maintenance programs is crucial for maintaining optimal ERW tube mill performance. Regular inspection and servicing of forming rolls, welding equipment, and drive systems help prevent unexpected downtime and ensure consistent product quality. Maintenance schedules should include detailed documentation of wear patterns, replacement intervals, and performance metrics.
Proper calibration of measuring instruments and control systems must be performed periodically to maintain accuracy. Special attention should be given to welding equipment maintenance, including regular inspection of contact rolls and cooling systems to ensure optimal welding performance.
Performance Optimization Techniques
Achieving maximum efficiency requires careful attention to operating parameters and production settings. Speed optimization, based on material properties and tube specifications, helps maximize output while maintaining quality standards. Regular analysis of production data enables identification of improvement opportunities and optimization of resource utilization.
Employee training programs play a vital role in optimization efforts. Operators must understand both the technical aspects of mill operation and quality control procedures to maintain high production standards. Implementation of lean manufacturing principles can further enhance operational efficiency and reduce waste.
Future Trends and Technological Advances
Digital Integration and Industry 4.0
The future of ERW tube mills lies in increased digital integration and smart manufacturing capabilities. Industry 4.0 technologies, including IoT sensors and cloud-based monitoring systems, are being incorporated to enable predictive maintenance and real-time quality control. Advanced analytics help optimize production parameters and predict potential issues before they impact production.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are being developed to enhance process control and quality assurance. These technologies enable automated adjustment of operating parameters based on historical data and current production conditions, leading to improved efficiency and product consistency.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Environmental considerations are driving innovations in ERW tube mill design and operation. New energy-efficient drive systems and improved welding technologies reduce power consumption while maintaining production capacity. Manufacturers are implementing recycling systems for cooling water and implementing waste reduction strategies throughout the production process.
The development of eco-friendly lubricants and cleaning solutions helps reduce environmental impact while maintaining high production standards. Integration of renewable energy sources and energy recovery systems further enhances the sustainability of tube manufacturing operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key advantages of ERW tube mills over other tube manufacturing methods?
ERW tube mills offer superior production speeds, excellent weld quality, and cost-effective operation compared to other methods. They provide consistent dimensional accuracy, efficient material utilization, and the ability to produce a wide range of tube sizes and specifications with minimal setup changes.
How does the welding process in ERW tube mills ensure joint integrity?
The high-frequency welding process used in ERW tube mills creates a forge-welded joint by heating the strip edges to fusion temperature and applying pressure to form a solid-state bond. The process is carefully controlled through precise temperature management and pressure application, resulting in a strong, consistent weld seam.
What maintenance practices are essential for optimal ERW tube mill performance?
Regular maintenance of forming rolls, welding equipment, and control systems is crucial. This includes proper lubrication, timely replacement of wear parts, calibration of measuring instruments, and regular inspection of critical components. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule and maintaining detailed service records helps ensure reliable operation and consistent product quality.