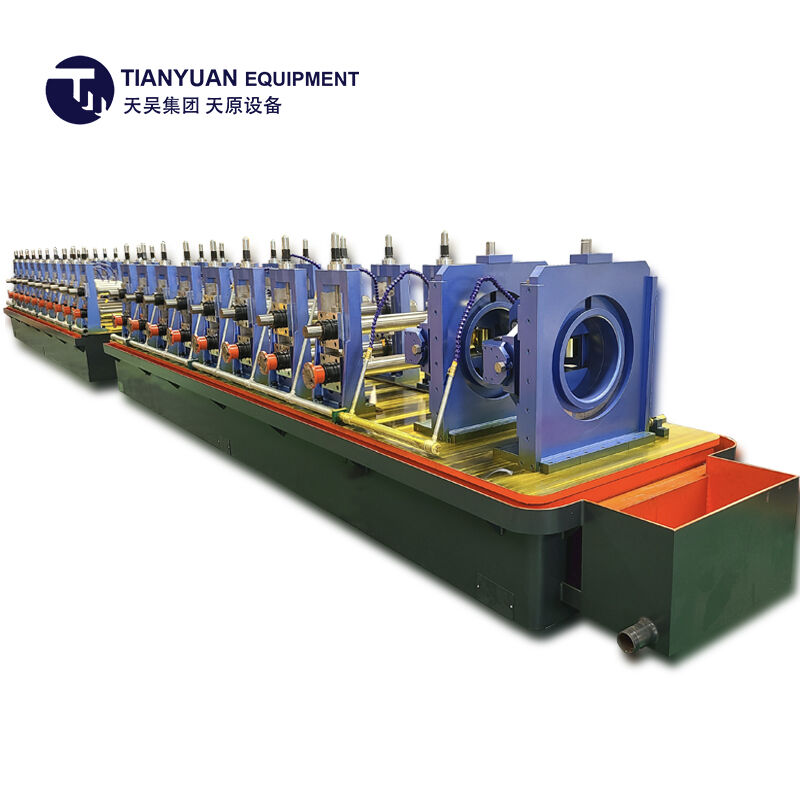
Modern industrial manufacturing demands efficient and precise solutions for pipe and tube production, making the selection of proper equipment crucial for operational success. The electric resistance welding process has revolutionized the tube manufacturing industry by offering superior speed, consistency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. An erw tube mill represents the pinnacle of this technology, providing manufacturers with the capability to produce high-quality welded tubes at unprecedented scales. These sophisticated machines integrate multiple processes into a single continuous operation, from material feeding to final sizing, ensuring optimal efficiency throughout the production cycle.
Understanding Electric Resistance Welding Technology
Fundamental Principles of ERW Processing
Electric resistance welding operates on the principle of generating heat through electrical resistance when current passes through metal surfaces in contact. The process begins with steel strips that are continuously fed into the mill, where they undergo precise forming through a series of rolls. As the formed tube edges meet, high-frequency electrical current creates localized heating at the seam, allowing the metal to reach welding temperature without melting. This controlled heating process ensures consistent weld quality while maintaining the structural integrity of the base material.
The erw tube mill system employs sophisticated control mechanisms to regulate current flow, pressure application, and welding speed. Temperature monitoring systems ensure optimal heat distribution along the weld seam, preventing overheating or insufficient fusion. Advanced mills incorporate real-time feedback systems that automatically adjust parameters based on material characteristics and production requirements. This level of automation reduces operator intervention while maintaining consistent product quality across extended production runs.
Advantages of ERW Technology Over Alternative Methods
Compared to seamless tube production or other welding methods, electric resistance welding offers significant advantages in terms of material utilization and energy efficiency. The process generates minimal waste since it works directly with steel coils, eliminating the need for piercing operations required in seamless tube manufacturing. Energy consumption remains relatively low due to the localized heating approach, which concentrates thermal energy precisely where welding occurs rather than heating entire tube sections.
Production speeds achievable with an erw tube mill far exceed those of alternative methods, with modern systems capable of producing hundreds of meters of tubing per minute. The continuous nature of the process eliminates start-stop cycles common in batch operations, contributing to higher overall equipment effectiveness. Quality consistency represents another major advantage, as the automated nature of ERW processing reduces variability associated with manual operations or semi-automatic systems.
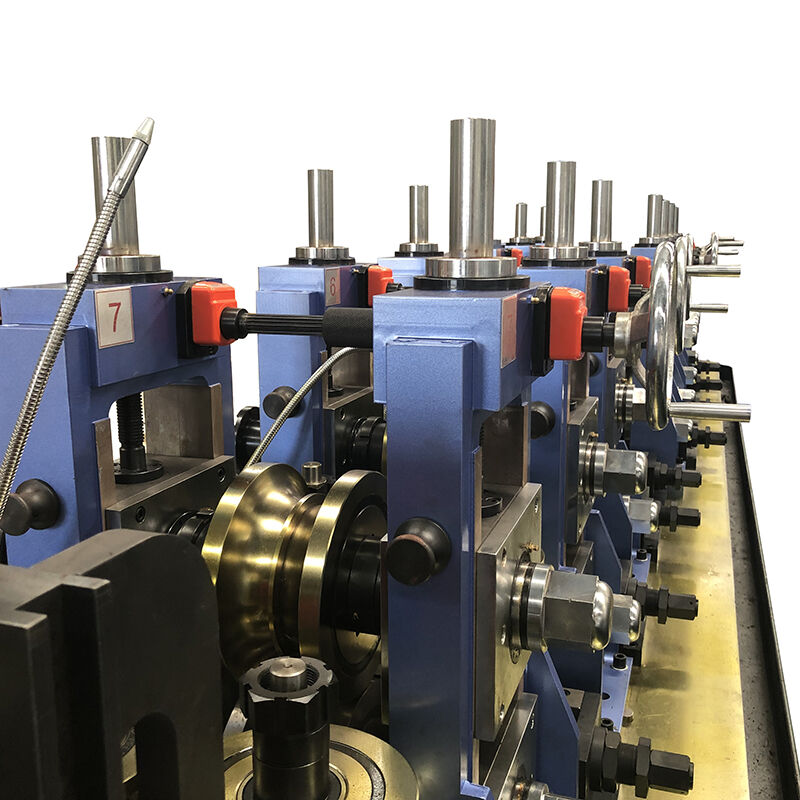
Key Components and System Architecture
Forming Section Design and Functionality
The forming section constitutes the heart of any erw tube mill, where flat steel strips transform into tubular shapes through progressive roll forming. Multiple forming stations guide the material through gradual bending operations, with each station contributing to the final tube geometry. Roll design optimization ensures smooth material flow while minimizing stress concentrations that could lead to surface defects or dimensional irregularities. Modern forming systems incorporate quick-change tooling to accommodate different tube sizes with minimal setup time.
Precision alignment systems maintain exact strip positioning throughout the forming process, preventing edge misalignment that could compromise weld quality. Advanced mills feature servo-driven roll positioning mechanisms that allow fine adjustments during operation, enabling operators to optimize forming parameters for different material grades or thickness variations. The forming section also includes edge preparation systems that ensure clean, square strip edges essential for high-quality welds.
Welding Station Configuration and Control Systems
The welding station represents the most critical component of the erw tube mill system, where electrical energy transforms adjacent metal edges into a continuous seam. High-frequency power supplies deliver precisely controlled electrical current through specialized electrodes or contacts positioned around the forming point. Welding pressure application systems ensure proper edge contact while maintaining consistent force distribution along the seam length. Temperature monitoring equipment provides real-time feedback on welding conditions, enabling automatic adjustments to maintain optimal parameters.
Modern welding stations incorporate multiple safety systems to protect both equipment and operators from electrical hazards and mechanical risks. Enclosed welding chambers contain electromagnetic emissions while providing access for maintenance and adjustment operations. Cooling systems manage electrode temperatures and prevent overheating of critical components during extended production runs. Automatic tube dimension monitoring ensures consistent geometry throughout the welding process, triggering corrections when deviations exceed predetermined tolerances.
Production Capabilities and Performance Metrics
Speed and Throughput Optimization
Production speed optimization in an erw tube mill involves balancing multiple factors including material properties, tube dimensions, and quality requirements. Modern systems achieve remarkable throughput rates by integrating advanced process control algorithms that continuously optimize welding parameters based on real-time conditions. Speed capabilities vary significantly based on tube diameter and wall thickness, with smaller tubes typically allowing higher production rates due to reduced material volume and faster heating cycles.
Throughput maximization requires careful coordination between material supply systems, forming operations, and downstream processing equipment. Buffer systems and accumulation capabilities ensure continuous operation even when upstream or downstream processes experience temporary interruptions. Advanced mills incorporate predictive maintenance systems that monitor equipment condition and schedule maintenance activities to minimize unplanned downtime, thereby maximizing overall equipment effectiveness and production capacity.
Quality Control and Dimensional Accuracy
Quality assurance in erw tube mill operations relies on comprehensive monitoring systems that track critical parameters throughout the production process. Dimensional measurement systems continuously verify tube diameter, wall thickness, and ovality to ensure compliance with specified tolerances. Weld seam inspection equipment employs various technologies including ultrasonic testing, eddy current examination, and visual inspection systems to detect potential defects before products leave the production line.
Statistical process control systems collect and analyze production data to identify trends and potential quality issues before they impact product specifications. Automated sorting and marking systems segregate products based on quality grades and customer requirements, ensuring proper product identification and traceability. Regular calibration procedures maintain measurement system accuracy, while operator training programs ensure consistent application of quality standards across all production shifts.
Material Compatibility and Application Range
Steel Grade Processing Capabilities
Modern erw tube mill systems demonstrate remarkable versatility in processing various steel grades, from standard carbon steels to high-strength low-alloy compositions. Material selection significantly impacts welding parameters, with different grades requiring specific current levels, welding speeds, and post-weld treatments. Low-carbon steels typically process easily with standard parameters, while high-strength grades may require modified welding conditions to achieve proper fusion without compromising mechanical properties.
Specialized steel grades such as corrosion-resistant alloys or weathering steels present unique processing challenges that advanced mills address through programmable parameter control systems. Material certification and traceability systems ensure proper documentation of steel grades throughout the production process, maintaining quality records required for critical applications. Pre-heating systems accommodate materials with specific thermal treatment requirements, while post-weld cooling controls manage microstructure development in heat-treatable grades.
Dimensional Range and Specification Flexibility
The dimensional flexibility of an erw tube mill determines its suitability for various market applications, with different mills optimized for specific size ranges. Small-diameter mills typically handle tubes from 6mm to 50mm outside diameter, while large-diameter systems process tubes exceeding 500mm diameter. Wall thickness capabilities vary proportionally, with specialized mills designed for either thin-wall applications or heavy-wall structural tubes requiring different forming and welding approaches.
Quick-change tooling systems enable rapid transitions between different tube sizes, minimizing setup time and improving production flexibility. Modular mill designs allow capacity expansion or size range modification through component upgrades rather than complete system replacement. Length cutting systems provide precise tube length control, while end-finishing equipment prepares tubes for specific application requirements including threading, beveling, or coupling attachment.
Installation and Commissioning Considerations
Facility Requirements and Infrastructure Planning
Successful erw tube mill installation requires comprehensive facility planning that addresses space requirements, utility needs, and material handling systems. Floor space calculations must account for not only the mill itself but also material storage areas, quality control stations, and finished product handling equipment. Structural foundations require precise engineering to support dynamic loads generated during high-speed operation while minimizing vibration transmission to adjacent equipment or building structures.
Electrical infrastructure planning encompasses high-power welding systems, motor drives, and control equipment that collectively represent significant electrical loads. Power quality considerations include harmonic mitigation and voltage regulation to ensure stable operation of sensitive electronic control systems. Compressed air systems, hydraulic power units, and cooling water circuits require careful sizing and redundancy planning to maintain continuous operation capabilities.
Commissioning Process and Performance Validation
The commissioning phase of an erw tube mill installation involves systematic testing and validation of all system components before full production begins. Initial mechanical alignment procedures ensure proper equipment positioning and eliminate potential sources of vibration or premature wear. Electrical system testing verifies proper operation of all control circuits, safety systems, and welding equipment under various operating conditions.
Performance validation testing demonstrates system capabilities across the intended operating range, confirming production speeds, quality levels, and dimensional accuracy. Material trials using representative steel grades establish optimal operating parameters while identifying any necessary adjustments to standard procedures. Operator training programs conducted during commissioning ensure production personnel understand proper operating procedures and safety protocols before independent operation begins.
Maintenance and Operational Excellence
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
Effective maintenance programs for erw tube mill operations focus on preventing unplanned downtime through systematic inspection and component replacement schedules. Critical components such as forming rolls, welding electrodes, and drive systems require regular monitoring to detect wear patterns before they impact product quality or cause catastrophic failures. Lubrication programs ensure proper bearing and gear performance while preventing contamination that could compromise system reliability.
Predictive maintenance technologies including vibration monitoring, thermal imaging, and oil analysis provide early warning of developing problems before they require emergency repairs. Spare parts inventory management ensures critical components remain available while minimizing carrying costs through optimized stocking levels. Maintenance planning software coordinates routine activities with production schedules to maximize equipment availability during peak demand periods.
Operational Optimization and Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement initiatives in erw tube mill operations focus on maximizing efficiency while maintaining quality standards and minimizing waste. Data collection systems monitor key performance indicators including production rates, quality metrics, and energy consumption to identify optimization opportunities. Statistical analysis of production data reveals trends and patterns that guide process improvements and parameter refinements.
Operator skill development programs ensure production personnel understand equipment capabilities and can recognize early signs of process variations that might impact product quality. Cross-training initiatives improve operational flexibility while building organizational knowledge about erw tube mill systems. Regular equipment upgrades and technology updates maintain competitive advantages while extending equipment useful life through modernization rather than replacement.
Market Applications and Industry Segments
Construction and Infrastructure Applications
The construction industry represents a major market segment for erw tube mill products, utilizing welded tubes in structural applications, mechanical systems, and infrastructure projects. Structural steel tubes produced by these mills meet stringent strength and dimensional requirements for building frameworks, bridges, and industrial facilities. Mechanical system applications include HVAC ductwork, handrailing, and architectural features where precise dimensions and consistent quality ensure proper fit and appearance.
Infrastructure development projects rely heavily on erw tube mill products for water distribution systems, gas pipelines, and electrical conduit applications. The combination of cost-effectiveness and reliability makes welded tubes particularly suitable for large-scale projects where budget considerations balance against performance requirements. Quality certification programs ensure products meet relevant industry standards and building codes across different geographic markets.
Automotive and Transportation Sector Demands
Automotive manufacturing represents a demanding application for erw tube mill products, requiring exceptional dimensional accuracy and consistent mechanical properties for safety-critical components. Exhaust system tubes must withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments while maintaining structural integrity throughout vehicle service life. Chassis components utilize high-strength welded tubes that provide optimal strength-to-weight ratios essential for modern vehicle design requirements.
Transportation sector applications extend beyond automotive to include railway systems, marine equipment, and aerospace components where specialized tube products meet unique performance requirements. Quality traceability systems ensure proper documentation of material properties and manufacturing processes required for critical applications. Advanced erw tube mill systems accommodate the tight tolerances and superior surface finishes demanded by transportation industry customers.
FAQ
What is the typical production capacity of an erw tube mill system
Production capacity varies significantly based on tube dimensions and mill configuration, with typical systems producing between 50 to 400 meters per minute depending on diameter and wall thickness. Smaller diameter tubes generally allow higher linear speeds, while larger diameter products require reduced speeds to maintain proper welding conditions. Modern high-speed mills can achieve annual capacities exceeding 100,000 tons when operating continuously with optimized parameters and minimal downtime.
How does an erw tube mill compare to seamless tube production in terms of cost and quality
ERW tube production typically offers lower manufacturing costs due to higher production speeds and better material utilization compared to seamless tube manufacturing. Quality differences are minimal for most applications, with modern erw tube mill systems producing tubes that meet or exceed seamless tube specifications for mechanical properties and dimensional accuracy. The choice between ERW and seamless products often depends on specific application requirements rather than inherent quality differences.
What maintenance requirements are critical for optimal erw tube mill performance
Critical maintenance activities include regular inspection and replacement of forming rolls, welding electrodes, and drive system components that experience continuous wear during operation. Lubrication system maintenance ensures proper bearing performance and extends equipment life, while cooling system maintenance prevents overheating of critical components. Preventive maintenance schedules typically recommend daily inspections, weekly lubrication services, and monthly comprehensive system checks to maintain optimal performance levels.
Can an erw tube mill process different steel grades and dimensions without major modifications
Modern erw tube mill systems feature flexible designs that accommodate different steel grades through parameter adjustments rather than hardware modifications. Quick-change tooling systems enable rapid transitions between different tube dimensions, typically requiring 2-4 hours for complete changeover depending on size differences. Material grade changes may require welding parameter adjustments and different post-weld treatments, but these modifications can usually be accomplished through software programming rather than physical equipment changes.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Electric Resistance Welding Technology
- Key Components and System Architecture
- Production Capabilities and Performance Metrics
- Material Compatibility and Application Range
- Installation and Commissioning Considerations
- Maintenance and Operational Excellence
- Market Applications and Industry Segments
-
FAQ
- What is the typical production capacity of an erw tube mill system
- How does an erw tube mill compare to seamless tube production in terms of cost and quality
- What maintenance requirements are critical for optimal erw tube mill performance
- Can an erw tube mill process different steel grades and dimensions without major modifications