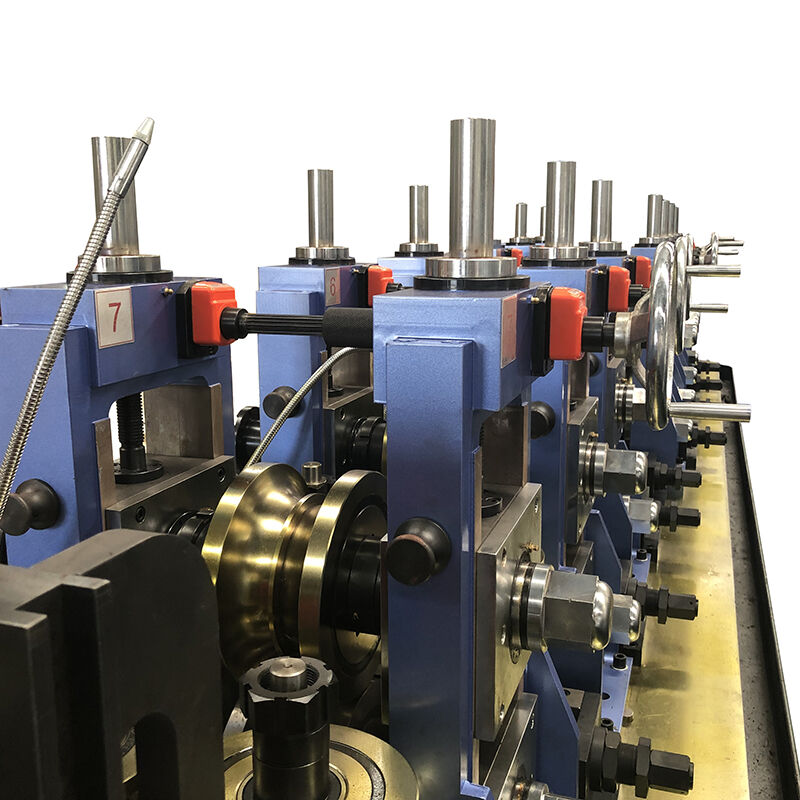
Наалтны цул зэс овоорхой үйлдвэрлэх нь тогтмол чанартай, зардлын хувьд үр дүнтэй байдлыг хангаж чадах дэвшилтэт машин тоног төхөөрөмж шаарддаг. ERW хоолойн үйлдвэр нь орчин үеийн хоолой үйлдвэрлэх технологийн оргил цэг бөгөөд инженерчлэлийн дэвшилтэт шийдлүүдийг найдвартай ажиллагаатай хослуулан хүнд шаардлагатай үйлдвэрийн стандартыг хангасан байдаг. Эдгээр тусгайлан бэлтгэсэн үйлдвэрлэлийн системүүд нь хоолой үйлдвэрлэх аргачлалыг хувиргасан бөгөөд хэмжээний нарийвчлал болон материалын шинж чанарын хувьд илүү нарийн удирдлагыг санал болгодог. Автомжуулсан удирдлагууд болон нарийн хэмжээний хэрэгслүүдийг нэгтгэснээр үйлдвэрлэгч бүрэн чанарын хатуу шаардлагыг хангасан, үйлдвэрлэлийн үр ашгийг хамгийн их байлгасан хоолойг гарган авдаг.
Орчин үеийн үйлдвэрлэл дэх ERW технологийг ойлгох
Цахилгаан эсэргүүцэлтэй налах үндсэн зарчим
Цахилгаан эсэргүүцлийн баглах нь өндөр үйлчилгээт бүх ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрлэлийн гол технологийг бүрдүүлдэг бөгөөд хяналттай цахилгаан гүйдлийг ашиглан металлографийн хувьд бат бөх баглалтыг үүсгэдэг. Энэхүү процесс нь зэсний хавтангийн ирмэгүүдийн хоорондох харилцан үйлчлэлийн цэг дээрх цахилгаан эсэргүүцлээр дулаан үүсгэж, нарийвчилсан хяналттай даралтанд доор түүхийн баглалт үүсгэдэг. Энэ технологи нэмэлт материал эсвэл хамгаалах хийн шаардлагыг арилгадаг тул орчин үеийн экологийн хувьд аюулгүй, зардал багатай үйлдвэрлэлийн шийдэл юм. Орчин үеийн системүүд нь янз бүрийн материалд тогтмол чанартай баглалт хангахын тулд температурын хяналт болон гүйдлийн удирдлагын нарийн механизмуудыг агуулсан байдаг.
Холбогчийн хүчийг сийрхий болгохын тулд милисекундын хугацаанд цахилгаан халтгай нь нарийвчлалтай цаг хугацаа ба даралтыг шаарддаг. Хөгжилдөө амжсан ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрийн загварууд нь материалын зузаан эсвэл найрлага дахь өөрчлөлтийг нөхөн тохируулах зорилгоор бодит цагт холилдох параметрийг хянах, тохируулах дижитал удирдлагын системийг агуулдаг. Энэ түвшний автоматжуулалт нь холилдох бүр нь механик чанар ба үргэлжлэх чадварын хувьд индустрийн стандартыг хангаж эсвэл давах боломжийг олгодог. Гарч буй холбоосууд нь анхны материалтай адил, эсвэл түүнээс илүү хүчтэй байдаг тул ERW хоолойг өндөр даралттай хэрэглээнд тохиромжтой болгодог.
Бусад материалуудын procession capabilities
Орчин үеийн ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрийн системүүд нь ердийн нүүрстөрөгчтэй гангаас эхлээд өндөр бат бөх чанартай хайлш болон найрлага хүртэлх гангуудын өргөн спектр, тодорхойлолтуудыг хүлээн авдаг. Материалын боловсруулалтын уян хатан чанар нь үйлдвэрийн тохиргооноос хамааран ихэвчлэн 0.5 мм-ээс 25 мм хүртэлх зузааны хязгаарт түгээн дэлгэрдэг. Энэ олон талт чанар нь барилга, автомашин, сойз, бүтээц техникийн салбаруудад үйлчилж чадах үйлдвэрлэгчдийг дэмждэг. Дэвшилтэт материал боловсруулах системүүд нь хэлбэржүүлэх явцад тогтмол хооллох хурд ба зураасны зөв байрлалыг хангана.
Орчин үеийн шахмалын загварчлалд нэвтрүүлсэн чанарын хяналтын арга хэмжээнүүд нь материал, хэмжээний нарийвчлалыг тасралтгүй хянах боломжийг олгодог. Шугамын доторх шалгалтын системүүд эцсийн бүтээгдэхүүний чанарт нөлөө үзүүлэхээс өмнө хазайлтуудыг илрүүлж, засдаг. Энэ нь хаягдалыг бууруулж, гарцын тодорхойлолтыг тогтвортой байлгахад тусалдаг. Олон төрлийн цайрын ангиллыг томоохон тохируулгын өөрчлөлтгүйгээр боловсруулах чадвар нь үйлдвэрлэлийн уян хатан байдлыг сайжруулж, бүтээгдэхүүн солих үеийн зогсонги байдлыг бууруулдаг. Энэхүү уян хатан чанар нь янз бүрийн чанарын шаардлагатай зах зээлийн хэсгүүдэд үйлчилдэг үйлдвэрлэгчдэд маш чухал болдог.
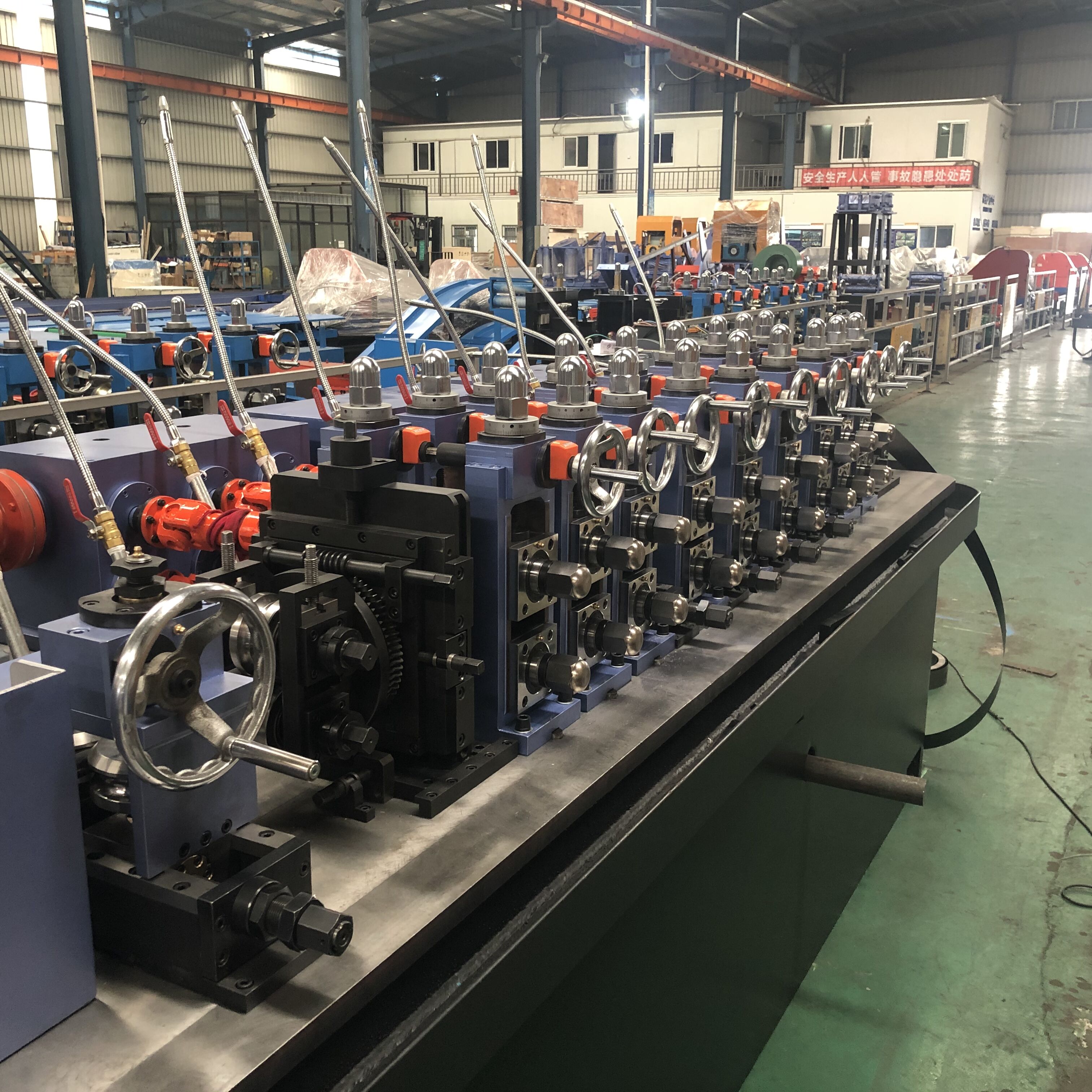

Техникийн үзүүлэлтүүд ба ажиллагааны параметрүүд
Үйлдвэрлэлийн багтаамж ба хурдны хяналт
Үйлдвэрийн зэрэглэлийн ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрийн суурилуулалтын үйлдвэрлэлийн хурд нь хоолойн диаметр, ханын зузаан, материал гэх мэт олон хүчин зүйлээс хамааран ихэд ялгаатай байдаг. Өндөр үзүүлэлттэй системүүд стандарт хэрэглээнд минутанд 100 метрээс дээш хурдтай үйлдвэрлэх чадвартай бөгөөд бүх процессийн туршид нарийн хэмжээний доторлогоог хадгалж чаддаг. Хувьсах давтамжийн хөдөлгүүр нь нарийвчлалтай хурдны удирдлагыг хангаж, ажилтан эдгээр материалын найрлага болон чанарын шаардлагад нийцүүлэн үйлдвэрлэлийн хурдыг тохируулах боломжийг олгодог. Үйлдвэрлэлийн хурд болон цэвэрлэлийн чанарын хоорондох харьцааг тогтвортой үр дүн гаргахын тулд анхааралтай тэнцвэртэй байлгах шаардлагатай.
Орчин үеийн шахмалын загварууд нь материал, гарах бүтээгдэхүүний шаардлагад үндэслэн автоматжуулан тохируулгыг хийдэг урьдчилан таамаглаж болох алгоритмуудыг агуулдаг. Эдгээр системүүд нь өмнөх үйлдвэрлэлийн өгөгдлийг шинжилж, шинэ үйлдвэрлэлийн циклд тохирох параметруудыг оновчтой болгох ба эхлэхэд зарцуулах цаг, материалын алдагдлыг шилжилтийн үед багасгадаг. Бодит цагт хяналт тавих боломж нь үйлдвэрлэлийн үр ашиг, чанарын үзүүлэлтэд немэх зөвлөмжийг үргэлж өгч, ашиглалтыг оновчтой түвшинд байлгах боломжийг олгодог. Industry 4.0 технологийг нэгтгэснээр үйлдвэрлэлийн харагдац, удирдлагын чадавхийг илүү сайжруулдаг.
Хэмжээний нарийвчлал ба чанарын стандарт
Тогтмол хэмжээний нарийвчлалд хүрэх нь мэргэжлийн аль ч үйлдвэрлэлийн хувьд шийдвэрчиг үзүүлэлт юм. эрвын түтүврийн бутлуур суурилуулга. Амралт орох төхөөрөмжүүд нь цөвөнгийн нарийвчлалыг нийтлэгийн туршид ±0.1 мм-ийн дотор байлгахын тулд нарийвчилсан машинжуулалттай хэрэгслүүдийг ашигладаг. Ханын зузаан нь ердийн тодорхойлолтоос ±5%-аас бага хэлбэлзэхийг ихэвчлэн хангаж, цор ганц хоолойн хэсгийн дагуу нь механик шинж чанарыг тогтвортой байлгах боломжийг олгодог. Эдгээр нарийн тодорхойлолт нь ажиллагааны түвшинг тогтвортой байлгахын тулд хүнд хэмжээний калибрын арга хэмжээ, тогтвортой засварын журмыг шаарддаг.
Чанарын баталгаажуулалтын системүүд нь орж ирсэн материал баталгаажуулахад эхлээд дуусах бүтээгдэхүүний шалгалт хүртэлх үйлдвэрлэлийн явцад олон шалгалтын цэгийг агуулдаг. Автомжуулсан хэмжилтийн системүүд чухал хэмжээсийг тасралтгүй хянах бөгөөд анхаарал шаардсан ямар ч хазайлтыг немед цахимоор мэдэгддэг. Статистик үйл явцын хяналтын алгоритмууд чанарын хандлагыг хянах, үйлдвэрлэлийн чанарт нөлөөлөхөөс өмнө боломжит асуудлыг урьдчилан таамагладаг. Баримтжуулалтын системүүд бүх чанарын хэмжилтийн бүрэн бүтэн түүхийг хадгалж, хяналтын шаардлагыг хангах, тасралтгүй сайжруулалтын арга хэмжээнд дэмжлэг үзүүлдэг.
Үйлдвэрлэлийн процессийн интеграци болон ажлын урсгал
Зуухны орцны бэлтгэл ба хоолойд оруулах систем
Үр дүнтэй зосисын бэлтгэл нь ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрийн амжилттай үйл ажиллагааны үндэс болдог бөгөөд тохиромжтой хайлтын чанарыг хангахын тулд ирмэгийн нөхцөлийг нарийвчлан тохируулах, гадаргууг бэлтгэх шаардлагатай. Автомжуулсан ороомог тэлэх систем нь материалыг хэлбэржүүлэх хэсэгт оруулах үед тасралтгүй таталтын хяналтыг хангаж, зосисын хэлбэр алдагдахаас эсвэл гадаргуу гэмтэхээс сэргийлдэг. Ирмэгийг тайрах үйлдэл нь хайлтанд муугаар нөлөөлж болзошгүй ямар ч жигд бус байдал эсвэл бохирдлыг арилгаж, урт үйлчилгээний хугацаатай өндөр нарийвчлалын таслагчийн хэрэгслүүдийг ашигладаг. Зосисыг холбох боломжийг нэгтгэснээр дараалсан ороомогуудыг холбож, үйлдвэрлэлд тасралт гаралгүй үргэлжлүүлэн ажиллах боломжийг олгодог.
Материалын хяналтын системүүд нь бэлтгэлийн явцад зурасны байршил болон чанарыг хянах бөгөөд анхаарал шаардсан асуудлуудын талаар бодит цагт мэдээлэл өгдөг. Агрегатын системүүд нь ороосон материал сунгах хурдны хэлбэлзлээс үл хамааран доод түвшнийн хэлбэржүүлэх үйл ажиллагаанд тогтмол эргэлтийн хурд бий болгохын тулд материалын урсгалын хэлбэлзлийг тэвчихдэг. Гадаргууг цэвэрлэх механизм нь бултуур, тосны үлдэгдэл болон бусад бохирдлыг арилгаж, бултуур болон гадаргуугийн төгсгөлийн чанарт нөлөөлөх боломжийг бууруулдаг. Эдгээр бэлтгэлийн алхмууд нь тогтмол үйлдвэрлэлийн үр дүн гаргах, чанарын холбоотой зогсолтыг хамгийн бага байлгахад чухал үүрэг гүйцэтгэдэг.
Хэлбэржүүлэх төвийн тохируулга ба хяналт
Хөгжин хэлбэр болон ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрийн технологийн цөмийг бүрдүүлдэг бөгөөд олон тооны хэлбэржүүлэх төхөөрөмжийг ашиглан хавтгай полосыг жигд дугуй хөндлөн огтлол болгон дарагдуулан хувиргадаг. Мөн өргөн хүрээтэй хоолойн диаметрийг нэг үйлдвэрт үйлдвэрлэх боломжийг олгохын тулд тохируулагч хэрэгсэл бүхий хэлбэржүүлэх төхөөрөмжийг суурилуулсан байдаг бөгөөд ихэвчлэн солих үед хамгийн бага өөрчлөлт шаарддаг. Хэлбэржүүлэх дараалал нь материалын стрессийг хамгийн бага байлгах, эцсийн бүтээгдэхүүний чанарыг муудуулах ирмэгийн гажилт эсвэл гадаргуугийн дутагдалд хүргэдэггүйн тулд нарийвчилсан инженерийн профайлын дагуу явагдана.
Серво-удирдлагатай байршилтын системүүд нь үйлдвэрлэлийн явцад хэлбэр өгөх роликнуудыг нарийвчлан тохируулах боломжийг олгох бөгөөд операторууд станцыг зогсоохгүйгээр хоолойн хэмжээсийг нарийвчлан тохируулах боломжтой болгодог. Хүчний мониторингийн системүүд нь тус бүрээр хэлбэр өгөх ачааллыг хянах замаар хэрэгсэл элэгдэх эсвэл материалын чанар өөрчлөгдөх зэрэг бүтээгдэхүүний чанарт нөлөөлж болзошгүй зүйлсийг цаг алдалгүй мэдэгдэдэг. Дэвшилтэт станцийн загваруудад тухайн хоолойн шаардлагаас хамааран хэлбэр өгөх хэрэгслүүдийг автоматаар байрлуулах боломжийг нэмж өгсөн бөгөөд ингэснээр тохируулгын хугацааг багасгаж, тохируулгын өөрчлөлт хийхэд операторын ур чадлын шаардлагыг хамгийн бага болгож өгдөг.
Чанарын хяналт болон шалгах аргачлал
Шугам дээрх шалгалтын технологи
Нэгэн зэрэг бага хэмжээний хооллох систем нь ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрийн шугамын дунд хяналтын системийг бодит цагт ашиглах замаар чанарын бүрэн хяналтаас эхэлдэг бөгөөд дэвсгэрэний хэмжээний хэлбэлзлийг илрүүлэхийн тулд хөгжилдөөт сенсорын технологийг ашигладаг. Лазерын хэмжилтийн системүүд хоолойн диаметр, ханын зузаан, өндийлтийн параметрүүдийг тасралтгүй хянах бөгөөд илрүүлсэн хазайлтуудыг автоматаар засварлахын тулд процессийн хяналтын системд немэх мэдээллийг нэн даруй илгээдэг. Дууны долгионгийн туршилтын боломж нь үйлдвэрлэлтийн урсгалыг таслахгүйгээр нийлмэлийн бат бөхийг шалгадаг бөгөөд бүх хоолой доод урсгалын боловсруулалт эсвэл боодолтын үйл ажиллагаанд орохоос өмнө бүтцийн шаардлагыг хангасан эсэхийг баталгаажуулдаг.
Харааны шалгалтын системүүд гадаргуугийн чанарыг шалгаж, хэрэглэгчийн зөвшөөрөл эсвэл дараагийн боловсруулалтын үйл ажиллагаанд нөлөөлөх боломжтой гадны дутагдал байдлыг илрүүлдэг. Эдгээр автоматжуулсан системүүд нийтлэг үйлдвэрлэлийн хурдаар ажиллах бөгөөд бүх үйлдвэрлэлийн сменд тогтмол үнэлгээний шалгуурыг хангаж, гар аргаар шалгах шаардлагыг арилгадаг. Мэдээллийн бүртгэлтийн боломж нь бүх шалгалтын үр дүнг бүрэн бүртгэж, үйлдвэрлэлийн хандлагын статистик шинжилгээ болон сайжруулах боломжийг тодорхойлоход тусалдаг. Загасны удирдлагын системтэй нэгдэх нь тохирохгүй бүтээгдэхүүнийг автоматаар хаях боломжийг олгох бөгөөд үйлдвэрлэлийн үргэлжлэх чадварыг хадгалж үлдээдэг.
Туршилтын стандартууд ба сертификатын шаардлагууд
Орчин үеийн ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрийн үйл ажиллагаа нь хоолойнуудын чанар, ажиллах чадварын талаарх олон улсын стандартуудын шаардлагад нийцэх ёстой. Шалгах аргачлал нь ихэвчлэн нийтлэг дээжид явуулдаг бөгөөд сунгалтын хүч, уян хатан чанар, суналтын хэмжээ зэрэг механик шинж чанарыг шалгадаг. Усны даралтанд оруулах туршилт нь хяналттай нөхцөлд хоолойн даралт тэсвэрлэх чадварыг баталгаажуулж, бүтээгдсэн бүтээгдэхүүн тодорхойлогдсон ажиллах даралтын түвшинд хангалттай аюулгүй байдлын захыг хангасан эсэхийг шалгадаг.
Гэрчилгээний шаардлагууд нь ихэвчлэн нефть, хий эсвэл бүтээцээр барьж буй салбарт ашиглах зэрэг чухал салбарын хувьд чанарын систем болон туршилтын аргачлалыг гуравдагч этгээдийн баталгаажуулалт шаарддаг. Баримтжуулалтын систем нь анхдагч материалд зориулсан гэрчилгээнээс эхлэн эцсийн шалгалтын үр дүн хүртэлх бүх мэдээллийн бүрэн хяналтыг хангаж, үйлчлүүлэгчийн чанарын шаардлагууд болон зохицуулалтын хариуцлагыг дэмждэг. Туршилтын тоног төхөөрөмжийн тогтмол калибрлалт нь хэмжилтийн нарийвчлал, найдвартай байдлыг хангах ба туршилтын аргачлалын баталгаажуулалт нь хамаарах стандарт, техникийн нөхцөл шаардлагад нийцэж байгааг баталдаг.
Хэрэглээ болон салбарын шаардлагууд
Барилгын болон бүтээцийн хэрэглээ
Барилгын үйлдвэр нь хэмжээний нарийвчлал болон тогтмол чанар шаардагдах бүтцийн хүрээ, тавиур, архитектурын хэрэглээнд ган хоолойг ашигладаг тэргүүлэх зах зээл юм. Бүтцийн инженерүүд нь тасралтгүй хоолойнуудтай харьцуулахад механик шинж чанар нь урьдчилан тодорхойлогдсон, өртөг харьцангуй бага байдаг тул ERW хоолойг сонгож ашигладаг бөгөөд ялангуяа дунд зэргийн даралт тэсвэрлэх шаардлага хангасан хэрэглээнд илүү тохиромжтой. Барилгын журам нэмэлтээр ERW хоолойн ажиллах чадварыг төлөвшүүлж байгаа бөгөөд урьд нь зөвхөн тасралтгүй бүтээгдэхүүнүүдэд л зөвшөөрдөг байсан даацын хэрэглээнд хүрээгээ өргөжүүлж байна.
Архитектурт хэрэглэх зүйлс нь орчин үеийн ERW хоолой үйлдвэрлэх технологийн дэвшилтэт боловсруулах, гадаргуугийн эд ангиудын тусламжтайгаар хангамжийн чанар болон хэмжээний нарийвчлалыг шаарддаг. Захидалт хэмжээ, техникийн шаардлагуудыг хийх чадвар нь инженер, архитекторуудад бүтцийн загварыг сайжруулах, цаашлаад гадны харагдацад тавигдах шаардлагуудыг хангах боломжийг олгодог. Гальванижуулалттай нийцэх чанар нь гадаа ашиглах тохиолдолд удаан хугацааны коррозоос хамгаалах боломжийг бий болгох бол өөр өөр гадаргуугийн боловсруулалт нь архитектурт хэрэглэгдэх олон төрлийн гадаргуугийн харагдацыг болон хамгаалалтын давхаргуудыг хангана.
Үйлдвэрлэлийн болон үйлдвэрлэлийн ашиглалт
Үйлдвэрлэлийн салбарууд нь найдвартай байдлыг шаардсан, зардал үр дүнтэй байх ёстой шингэн зөөвөрлөх систем, пневматик хэрэглээ, машин механизмийн барилга байгууламжид ERW хоолойг ашигладаг. Нарийн төвөгтэй ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн нарийвчлалтай хэмжээсийн нарийвчлал нэмэлтээр машинд оруулах эсвэл хэмжээ тохируулах үйлдэл хийлгүйгээр нарийн төвөгтэй цуглуулгын үйл явцыг хангана. Дулааны боловсруулалтын боломжоор үйлдвэрлэгчид өндөр бат бөх чанар эсвэл сайжруулсан хэлбэржүүлэх чадвар зэрэг тусгай зориулалтын хэрэглээнд шаардагдах тодорхой механик шинж чанарыг олж авах боломжтой болгодог.
Боловсруулалт үйлдвэрийн салбар нь шидгрэгч шийдлийнхээс илүү нийт зардлын давуу талаар давуу талыг хэрэгжүүлж, шаардлагатай ажиллагааны шаардлагыг хангахын тулд ERW хоолойг бага-дунд зэсийн шингэний системд ашигладаг. Зузаан ханын зах зузаан хослуудыг зах зузаан хослуудыг үйлдвэрлэх чадвар нь тухайн даралт, урсгалтын шаардлагад нийцүүлэн системийн загварыг үр дүнтэй болгож байна. Чанарын гэрчилгээний хөтөлбөрүүд нь ажиллагааны зөвшөөрөлд мэдээллийн хандалт, ажиллагааны баталгаажуулалт шаардлагатай бол баталгаажуулалтад зориулсан салбарт ашиглахыг дэмждэг.
Засвар үйлчилгээ болон үйл ажиллагааны гавьяа
Эрэмбэлэн барих програм
Амжилттай ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрийн ажиллагаа нь тогтмол үйлдвэрлэлийн чадавх болон бүтээгдэхүүний чанарыг хангахын тулд механик бүрэлдэхүүн хэсгүүд болон хяналтын системийг хамарсан нэгдсэн урьдчилан сэргийлэх техникийн үйлчилгээний хөтөлбөр шаарддаг. Үйлдвэрлэлийн тонн эсвэл ажилласан цагт суурилсан төлөвлөсөн техникийн үйлчилгээ нь хүлээгдээгүй гэмтлийг сэргийлж, хэрэгслүүдийн ашиглалтын хугацаа болон системийн үйл ажиллагааг сайжруулдаг. Смазкийн хөтөлбөрүүд нь орчин үеийн хоолойн үйлдвэрийн өндөр хурд, их ачаалалтай нөхцөлд тохирсон дэвшилтэт синтетик смазкийг ашигладаг бөгөөд бүрэлдэхүүн хэсгийн амьдралыг уртасгаж, техникийн үйлчилгээний давтамжийг бууруулдаг.
Урьдчилан таамаглаж болох засвар үйлчилгээний технологи нь хөдөлгөгчийн бүрэлдэхүүн хэсгүүдийг чичирхийллийн шинжилгээ, дулааны зураг авах, тосны шинжилгээний аргуудаар хянах замаар үйлдвэрлэлд нөлөө үзүүлэхээс өмнө асуудлыг илрүүлдэг. Эдгээр технологиуд нь нөхцөл байдлын үндсэн дээр засвар үйлчилгээний хуваарь тодорхойлох боломжийг олгох бөгөөд ресурсын ашиглалтыг үр дүнтэй болгох, төлөвлөгөөгүй зогсолтыг хамгийн бага болгоход тусалдаг. Баримтжуулалтын системүүд нь засвар үйлчилгээний үйл ажиллагаа, бүрэлдэхүүн хэсгийн ажиллагааг хянах бөгөөд үнэмлэхүйн хэрэглээ, гэмтлийн хэв маягийн үндсэн дээр хэрэгслэлтийн материал, хэрэгслийн нөөцийг үр дүнтэй болгоход дэмжлэг үзүүлдэг.
Ажилтны дамжуулалт болон эмнэлгийн протокол
Нийлмэл ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрлэлийн тоног төхөөрөмжийг үр дүнтэй ажиллуулахын тулд техникийн ажиллагааны журмаас гадна хүний ба тоног төхөөрөмжийн хамгаалалтад чухал ач холбогдолтой аюулгүй байдлын протоколыг хамарсан нягтлан ажиллагчдын сургалтын програмууд шаардлагатай. Сургалтын хөтөлбөрт тохируулга, чанарын хяналтын аргачлал, гэм зэмийг илрүүлэх арга зүй, аюултай нөхцөл байдалд урьдчилан сэргийлэх арга зам зэрэг аюулгүй, үр ашигтай үйлдвэрлэлийн үйл ажиллагаанд шаардлагатай асуудлуудыг хамрах ёстой. Бодит үйлдвэрлэлийн тоног төхөөрөмжийг ашиглан хийгдэх гар ажиллагааны сургалт нь ажиллагчид практик ур чадвар эзэмшихэд туслаж, процессийн параметр болон бүтээгдэхүүний чанарын хоорондын холбоог ойлгоход нь хүргэдэг.
Аюулгүй байдал хангах арга хэмжээнд машин тоноглолын хамгаалалт, түгжих/шошго тавих арга хэмжээ, эв гэмгүй үед зогсоох боломжийг хамруулан хүмүүсийг ердийн үйл ажиллагаа болон засвар үйлчилгээний үеэр хамгаалах зорилгоор хэрэгжүүлдэг. Тогтмол аюулгүй байдлын шалгалтууд нь батлагдсан арга хэмжээнд нийцсэн байдлыг шалгаж, аюулгүй байдал хангах систем болон арга хэмжээний сайжруулах боломжийг тодорхойлдог. Үргэлжлэх сургалтын хөтөлбөрүүд нь ажиллуулагчдыг шинэчлэгдэж буй технологи болон аюулгүй байдлын стандартын талаар мэдээлэлтэй байлгаж, объектын нийт амьдралын мөчлөгийн туршид зохицуулалтанд нийцэх, мөн үйл ажиллагааны онцлох зорилготой нийцүүлэхэд дэмжлэг үзүүлдэг.
Түгээмэл асуулт
ERW хоолойны үйлдвэрийн үйлдвэрлэлийн чадал ямар хүчин зүйлсээс хамаарах вэ
Үйлдвэрлэлийн чадал нь хоолойн диаметрийн хүрээ, ханын зузаан, материалын ангилал болон шаардагдах чанарын түвшин гэх мэт хэд хэдэн гол хүчин зүйлсээс хамаарна. Ихэвчлэн том диаметртэй хоолойнууд нь хэлбэржилтийн чанарыг хадгалахын тулд удаан үйлдвэрлэлийн хурд шаарддаг бөгөөд ханын зузаан ихтэй материалын хувьд зохистой багтаахуйн үйл явцыг хангахын тулд хурдыг багасгах шаардлагатай байдаг. Хэмжээний дагуу хэлбэржүүлэх тогломуудын тоо, цахилгааны чадал зэргийг багтаасан ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрлэлийн тоног төхөөрөмжийн байгууламж нь хамгийн ихдээ хүрч болох үйлдвэрлэлийн хурдад шууд нөлөөлдөг. Ахмад удирдлагын системүүд нь материалын шинж чанар, зорилтот техникийн шаардлагуудад үндэслэн хурдны тохируулгийг автоматаар оновчтой болгох замаар чанарын стандартыг хадгалж, гарц-гаргалтыг хамгийн их байлгах боломжийг олгодог.
ERW багтаахтай харьцуулахад бусад хоолой үйлдвэрлэх аргууд ямар ялгаатай вэ
ERW баглаачийн хувьд зүйрлэх боломжгүй хоолойгоор үйлдвэрлэхтэй харьцуулахад өртөг, үйлдвэрлэлийн үр ашгийн хувьд томоохон давуу талуудтай байдаг бөгөөд спираль зууралтын хувилбартай харьцуулахад хэмжээний удирдлагын хувьд илүү сайн байдаг. Энэ процессын дүнд зүйрлэх боломжгүй үйлдвэрлэлд шаардагдах үнэтэй прокатлах үйлдлүүдийг ашиглах шаардлагагүй болдог бөгөөд энэ нь энерги хэрэглээ, анхдагч материал алдагдах хэмжээг бууруулдаг. Орчин үеийн ERW хоолойны үйлдвэрийн технологи нь зүйрлэх боломжгүй хоолой шаарддаг байсан олон төрлийн хэрэглээг хангах эсвэл давах чанартай зууралт үүсгэж чаддаг бөгөөд зах зээлийн боломжийг өргөжүүлж, өрсөлдөхүйц үнийн давуу талыг хадгалж байдаг. Орчин үеийн ERW хоолойны үйлдвэрийн технологи нь зүйрлэх боломжгүй хоолой шаарддаг байсан олон төрлийн хэрэглээг хангах эсвэл давах чанартай зууралт үүсгэж чаддаг бөгөөд зах зээлийн боломжийг өргөжүүлж, өрсөлдөхүйц үнийн давуу талыг хадгалж байдаг. Экологийн давуу талуудад бусад зуурамтгай хоолойнуудын үйлдвэрлэлд шаардагдах энергийн хэрэглээг бууруулах, зуурамтгай материалыг ашиглах шаардлагагүй болгох нь хамаарагдана.
Ямар засвар үйлчилгээний шаардлага оптималь ажиллагааг хангахад чухал үүрэг гүйцэтгэдэг вэ
Шүргэлтэн дохиулах системийн байнгын тохируулга, хэлбэржүүлэх багажны износон байдлын дагуу тогтмол солилт болон мельд дахь өндөр хурдны хэсгүүдийг бүрэн хэмжээгээр смазк хийх нь чухал засвар үйлчилгээний хэсгүүд юм. Цацраг холболтын электродын засвар үйлчилгээ нь зэвсэггүй цацраг холболтын чанарыг тогтвортой байлгахад чухал бөгөөд үйлдвэрлэлийн тоннажийн зааврын дагуу байнгын цэвэрлэлт, солилт шаардлагатай. Хэлбэржүүлэх роликийн байдал нь хоолойн чанарт шууд нөлөөлдөг тул тогтмол шалгалт, хэмжилтийн аргаар хянах шаардлагатай. Хяналтын системийн тохируулга нь процессын параметрийн нарийн удирдлагыг хангаж, үйлдвэрлэгчийн зөвлөсөн давтамж, аргачлалыг дагах ёстой.
Орчин үеийн ERW хоолойн мельдийн системүүд онцгой зэвсгийн маркийг боловруулах чадвартай юу
Орчин үеийн ERW хоолойн үйлдвэрийн загварууд нь өндөр бат бөх чанарын бага хайлшт болор, цэвэр мөнгөн бохир, янз бүрийн давхаржсан материалын зэрэг тусгай зэрэглэлийн болорын өргөн спектрийг системийн тохируулга хийснээр ашиглах боломжийг олгодог. Дэвшилтэт цахилгаан бултуургын удирдлага нь янз бүрийн материалд тохирох параметрийг тохируулж, ялгаатай болорын зэрэглэл бүрийн хувьд бултуургын гүн ба холболтын бат бөх чанарыг хангана. Зарим тусгай хэрэглээнүүд нь цэвэр мөнгөн бохирд зориулсан сайжруулсан цэвэрлэх систем эсвэл өндөр бат бөх чанарын материалд зориулсан хэлбэр өгөх дарааллыг өөрчлөх зэрэг нэмэлт тоног төхөөрөмж шаардаж болзошгүй. Тоног төхөөрөмжийн үйлдвэрлэгчтэй зөвлөлдөх нь тухайн тусгай зэрэглэлийн шаардлагад нийцүүлэн тодорхой чадавхи болон шаардлагатай өөрчлөлтийг тодорхойлоход тусална.
Гарчиг
- Орчин үеийн үйлдвэрлэл дэх ERW технологийг ойлгох
- Техникийн үзүүлэлтүүд ба ажиллагааны параметрүүд
- Үйлдвэрлэлийн процессийн интеграци болон ажлын урсгал
- Чанарын хяналт болон шалгах аргачлал
- Хэрэглээ болон салбарын шаардлагууд
- Засвар үйлчилгээ болон үйл ажиллагааны гавьяа
-
Түгээмэл асуулт
- ERW хоолойны үйлдвэрийн үйлдвэрлэлийн чадал ямар хүчин зүйлсээс хамаарах вэ
- ERW багтаахтай харьцуулахад бусад хоолой үйлдвэрлэх аргууд ямар ялгаатай вэ
- Ямар засвар үйлчилгээний шаардлага оптималь ажиллагааг хангахад чухал үүрэг гүйцэтгэдэг вэ
- Орчин үеийн ERW хоолойн мельдийн системүүд онцгой зэвсгийн маркийг боловруулах чадвартай юу